
VB.Net to C Sharp Converter 1.3 serial key or number

VB.Net to C Sharp Converter 1.3 serial key or number
Table of consents:
Converting codes Focus on upgrading VB6 to VB.Net and converting C# <=> VB.Net, and listing many other helpful converter including php, java & others.
Downloads of C# & VB.Net Converters Using NRefactory v4:
Downloads of C# & VB.Net Converters Without Using NRefactory v4:
Downloads of VB6 Upgrader:
Downloads of C# & VB Helper Library & related code:
Downloads of PHP to .NET:
Downloads of Java & .NET:
Downloads of C++ to .NET:
Downloads of ColdFusion to .NET:
- Make sure your code can be recompiled and run well before start converting.
- For C# and VB.Net 100% code conversion maybe get in many causes but not always. In many cases many post conversion fixing is required.
- No convertors can grantee the 100% conversion.
- For other language pairs: Make sure the the target language support your project type.
- Please note the VB6 converting is a hard work because of the programing language philosophy is defer. please see VB6 section later is this article
SharpDevelop:
Lots of C# <> VB code converter are available all most all of them are using Refactory library form SharpDevelop IDE to make the conversion and them make some useful post conversion fixing.
The power of NRefactory v4 is parsing the code before the conversion; even if a keyword could take more than one meaning it could be converted correctly because of understanding the code line before the conversion. an other thing will make the converting is possible in most cases.
About SharpDevelop
- It's an freeware Open Source Development Environment for .NET.
- It could be used to make many useful code conversion.
- SharpDevelop IDE is the mother of NRefactory v4 library which is the most uses converting library
- The conversion that done using SharpDevelop IDE is much beater.
- It provide a wide range of code conversion C#, VB.NET, Boo, Python, Ruby
About NRefactory v4:
- ICSharpCode.NRefactory is freely available as a part of SharpDevelop IDE v4.
- It is parser library for C# and VB.
- It consists of a single Abstract Syntax Tree (AST) that can represent all constructs that are available in C# or VB (unlike System.CodeDom, which only represents constructs common to C# and VB).
- By using the C# parser and a VB output visitor (or vice versa), you can do a code converter.
- After parsing to AST, you can analyze and/or transform the AST and re-create source code from the (modified) AST, then re-insert the comments we saved from the parser into the output
- For more info about NRefactory v4 please see: sharpdevelop.net and NRefactory wiki.
- You may try samples\NRefactoryDemo in the SharpDevelop source code to take a look how the AST parse source code.
About AST and Parsing:
The following example show a simple parsing proses.
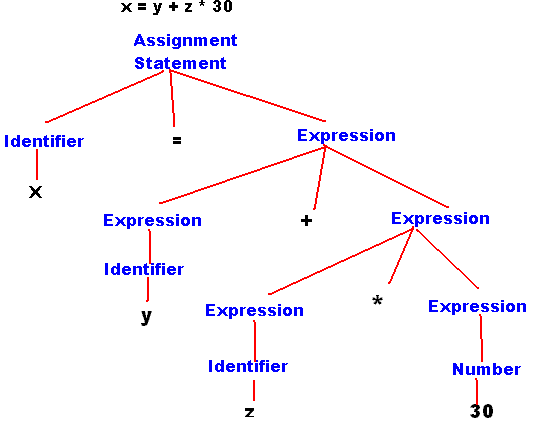
SharpDevelop IDE and C# VB converters:
| Application | Conversion Technique | What to convert | Conversion | Notes |
| SharpDevelop IDE | Developer IDE freeware | Code & file | C#, VB.Net, boo, Python, Ruby | |
| VB.Net to C# Converter | Use NRefactory v4 | Code & file | VB.Net > C# | |
| Convert .NET | Use NRefactory v4 | Code only | C# <> VB.Net | |
| C# to VB.NET Project Converter | Use NRefactory v4 | Projects | C# > VB.Net | |
| Instant VB | Share ware Internal Converter | Code, file & folder | Special version for each conversion convert between: C#, VB.Net, C++, Java | Very Flexible |
What in C# that has no equivalent is VB:
- C# Fixed-size buffers and fixed statement has no equivalent in VB: privatefixedchar name[30]
- C# fixed block has no equivalent in VB:
Enter the fixed keyword. When used for a block of statements, it tells the CLR that the object in question cannot be relocated, and thus, it ends up pinning the object. Thus, when pointers are used in C#, the fixed keyword is used pretty often to prevent invalid pointers at runtime. - C# Generic indexers and properties has no equivalent in VB: public T this[string key] { get { /* Return generic type T. */ } } public T GetItem<T>(string key) { /* Return generic type T. */ }
- C# Generic operators has no equivalent in VB: publicstatic T operator +<T>(T a, T b) { // Do something with a and b that makes sense for operator + here }
- C# #undef has no equivalent in VB.
- C# volatile/checked/unchecked/stackalloc has no equivalent in VB:
Using the unchecked statement with constant expressions Overflow is unchecked at compile time or run time and the return value be deffer - C# unsafe block has no equivalent in VB: unsafestaticvoid FastCopy ( byte[] src, byte[] dst, int count ) { // unsafe context: can use pointers here }
- C# extern alias has no equivalent in VB:
It can sometimes be necessary to reference two versions of assemblies that have the same fully-qualified type names, for example when you need to use two or more versions of an assembly in the same application. By using an external assembly alias, the namespaces from each assembly can be wrapped inside root-level namespaces named by the alias, allowing them to be used in the same file
To reference two assemblies with the same fully-qualified type names, an alias must be specified on the command line, as follows: /r:GridV1=grid.dll /r:GridV2=grid20.dll This creates the external aliases GridV1 and GridV2. To use these aliases from within a program, reference them using the extern keyword. For example: externalias GridV1; externalias GridV2; - C# overloading ++ or -- operator in has no equivalent in VB: ++ & -- can converted easily but overloading is not.
- C# ?? operator has no equivalent in VB
What in VB that has no equivalent is C#:
- VB parameterized properties has no equivalent in C# PublicProperty MyProperty(ByVal A AsString) AsStringGetReturn2 * A EndGetSet(ByVal value AsString) A = value / 2EndSetEndProperty
- VB Numeric labels, On Error, Resume Next, Continue and Err object has no equivalent in C# Sub Test() OnErrorResumeNext Err.Raise(1000) OnErrorGoTo0 Err.Raise(1001) OnErrorGoTo -1 Err.Raise(1002) OnErrorGoTo EH Err.Raise(1003) ExitSub EH: MsgBox(Err.Description) ResumeNextEndSub
- VB IIf is some who defer than if in C#. A = IIf(E, B, A)
- VB ReDim Preserve has no built-in equivalent in C# ReDim Preserve A(9)
- VB Select Case: switch is not as flexible as Select Case and many VB Select Case blocks cannot be converted to switch SelectCase A Case1To10'CaseIs < 2 * A 'CaseIs > 30'EndSelect
- VB Procedures local static variables has no built-in equivalent in C# but class-level private variable may used. Sub Test() Static InUse AsBoolean = FalseIf InUse ThenExitSub'Run Once code InUse = True'EndSub
- VB With has no equivalent in C#. WithMe .Width = 10 .Top = 0EndWith
- VB Import Shared Class member is not supported in C# Imports WindowsApplication1.Form1
- VB Exit try
- VB Exit statements that not matching the immediately enclosing block.
- VB Member names can be the same as their enclosing type but in C# can't.
- VB #Const can be set to any value but in C# accept constants only #Const C = 2 * A
- VB MyClass has no equivalent in C# (some time using this is OK)
- In C#, an object cannot reference itself in its class-level declarations: You cannot use this in class-level declarations in C#.
- In C#, an object cannot reference its base class in its class-level declarations: You cannot use base in class-level declarations in C#.
- Numeric labels are not allowed in C#: You must change the label to be a standard C# identifier.
- VB &O has no equivalent in C#
- VB When has no equivalent in C#
- VB has some operator that are not present in C# and can't be overloaded in C# in any way such as(integer division (VB \), Like, exponentiation (VB ^))
- VB Method with the same name as the Class name is used for constructor in C# and can't use for any other in C#.
- VB integer casts convert 'True' to -1, but System.Convert methods convert 'True' to 1.
C# and VB Language Equivalents and Comparison:
- Language Equivalents
- Comparison of C# and VB
- Complete Comparison for VB.NET & C#
Using SharpDevelop as a code converter:
- Run SharpDevelop IDE
- From file menu select open - project/solution and open the project to be converted
- From View menu select projects
- In the project window select the project to be converted
- from project menu choose convert and then choose the target language
- This will convert the whole project
- The conversion could be done by right clicking the project icon in the project window then choose convert
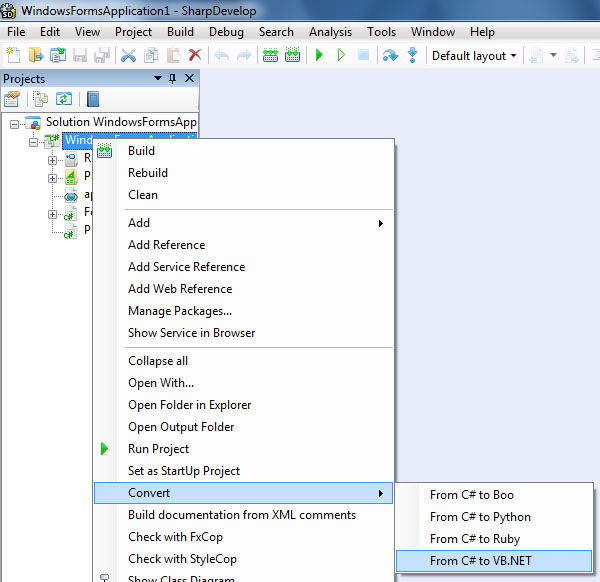
SharpDevelop Points of Interest
How to covert C# code:
The code is converted using class:
Converter code in VB:
Imports ICSharpCode.NRefactory Imports ICSharpCode.NRefactory.PrettyPrinter Imports System.IO PublicClass CS2VB PublicOverridesFunction ConvertCode(ByVal sourceCode AsString) AsStringDim specials As IList(Of ISpecial) Dim result As Ast.CompilationUnit Dim Parse_errors = ""Using parser As IParser = ParserFactory.CreateParser( _ SupportedLanguage.CSharp, New StringReader(sourceCode)) parser.Parse() 'this allows retrieving comments, preprocessor directives, etc. '(stuff that isn't part of the syntax) specials = parser.Lexer.SpecialTracker.RetrieveSpecials() 'this retrieves the root node of the result AS result = parser.CompilationUnit If parser.Errors.Count > 0Then Parse_errors = parser.Errors.ErrorOutput EndIfEndUsing'Now you can analyze and/or transform the AST.'Should you want to re-create source code from the (modified) AST, 'use an output visitor: 're-insert the comments we saved from the parser into the outputDim outputVisitor AsNew PrettyPrinter.VBNetOutputVisitor Dim astViewUnit = result Using SpecialNodesInserter.Install(specials, outputVisitor) astViewUnit.AcceptVisitor(outputVisitor, Nothing) EndUsingDim outputCode = outputVisitor.Text 'By using the C# parser and a VB output visitor (or vice versa), 'you can build a code converter. Of course, 'the real Code Converter in SharpDevelop also transforms the AST to fix cases 'where C# and VB semantics differ.Return outputCode EndFunctionEnd Class/pre>Converter code in C#:
using ICSharpCode.NRefactory; using ICSharpCode.NRefactory.PrettyPrinter; using System.IO; publicclass CS2VB { publicoverridestring ConvertCode(string sourceCode) { //var names and format is as in http://wiki.sharpdevelop.net/NRefactory.ashx//ICSharpCode.NRefactory is a parser library for C# and VB.//It consists of a single Abstract Syntax Tree (AST) //that can represent all constructs that are available in C# or VB //(unlike System.CodeDom, which only represents constructs common to C# //and VB).//Please try samples\NRefactoryDemo in the SharpDevelop source code //to take a look at the AST//To parse source code, use: IList specials; Ast.CompilationUnit result; object Parse_errors = ""; using (IParser parser = ParserFactory.CreateParser(SupportedLanguage.CSharp, new StringReader(sourceCode))) { parser.Parse(); // this allows retrieving comments, preprocessor directives, etc. //(stuff that isn't part of the syntax) specials = parser.Lexer.SpecialTracker.RetrieveSpecials(); // this retrieves the root node of the result AST result = parser.CompilationUnit; if (parser.Errors.Count >0) { MessageBox.Show(parser.Errors.ErrorOutput, "Parse errors"); } } //Now you can analyze and/or transform the AST.//Should you want to re-create source code from the (modified) AST, //use an output visitor: //re-insert the comments we saved from the parser into the output PrettyPrinter.VBNetOutputVisitor outputVisitor = new PrettyPrinter.VBNetOutputVisitor(); object astViewUnit = result; using (SpecialNodesInserter.Install(specials, outputVisitor)) { astViewUnit.AcceptVisitor(outputVisitor, null); } object outputCode = outputVisitor.Text; //By using the C# parser and a VB output visitor (or vice versa), //you can build a code converter. Of course, //the real Code Converter in SharpDevelop also transforms the AST //to fix cases //where C# and VB semantics differ.return outputCode; } }Demo conversion:
Partial code convert is not supported code should be in class and in method.
Demo1:
class Class1{void sub1(){ //your code startint x =0; //your code end }}The result in VB
Class Class1 Sub sub1() 'your code startDim x AsInteger = 0'your code endEndSubEndClassDemo 2:
namespace WindowsFormsApplication1{ partialclass Form1 { private System.ComponentModel.IContainer components = null; private System.Windows.Forms.TextBox textbox1; private System.Windows.Forms.TextBox textbox2; protectedoverridevoid Dispose(bool disposing) { if (disposing && (components != null)) { components.Dispose(); } base.Dispose(disposing); } privatevoid InitializeComponent() { this.textbox1 = new System.Windows.Forms.TextBox(); this.textbox2 = new System.Windows.Forms.TextBox(); this.SuspendLayout(); //// textbox1//this.textbox1.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(30, 30); this.textbox1.Name = "TEXTBOX1"; this.textbox1.Size = new System.Drawing.Size(80, 20); this.textbox1.TabIndex = 0; //// textbox2//this.textbox2.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(30, 60); this.textbox2.Name = "textbox"; this.textbox2.Size = new System.Drawing.Size(80, 20); this.textbox2.TabIndex = 1; this.textbox2.TextChanged += new System.EventHandler(this.textbox_TextChanged); //// Form1//this.AutoScaleDimensions = new System.Drawing.SizeF(6F, 13F); this.AutoScaleMode = System.Windows.Forms.AutoScaleMode.Font; this.ClientSize = new System.Drawing.Size(284, 262); this.Controls.Add(this.textbox2); this.Controls.Add(this.textbox1); this.Name = "Form1"; this.Text = "Form1"; this.ResumeLayout(false); this.PerformLayout(); } public Form1() { InitializeComponent(); } privatevoid textbox_TextChanged(object sender, EventArgs e) { string x = ""; string X = ""; } } }The result in VB
Namespace WindowsFormsApplication1 PartialClass Form1 Private components As System.ComponentModel.IContainer = NothingPrivate textbox1 As System.Windows.Forms.TextBox Private textbox2 As System.Windows.Forms.TextBox ProtectedOverridesSub Dispose(disposing AsBoolean) If disposing AndAlso (components IsNotNothing) Then components.Dispose() EndIfMyBase.Dispose(disposing) EndSubPrivateSub InitializeComponent() Me.textbox1 = New System.Windows.Forms.TextBox() Me.textbox2 = New System.Windows.Forms.TextBox() Me.SuspendLayout() '' textbox1'Me.textbox1.Location = New System.Drawing.Point(30, 30) Me.textbox1.Name = "TEXTBOX1"Me.textbox1.Size = New System.Drawing.Size(80, 20) Me.textbox1.TabIndex = 0'' textbox2'Me.textbox2.Location = New System.Drawing.Point(30, 60) Me.textbox2.Name = "textbox"Me.textbox2.Size = New System.Drawing.Size(80, 20) Me.textbox2.TabIndex = 1AddHandlerMe.textbox2.TextChanged, New System.EventHandler(AddressOfMe.textbox_TextChanged) '' Form1'Me.AutoScaleDimensions = New System.Drawing.SizeF(6F, 13F) Me.AutoScaleMode = System.Windows.Forms.AutoScaleMode.Font Me.ClientSize = New System.Drawing.Size(284, 262) Me.Controls.Add(Me.textbox2) Me.Controls.Add(Me.textbox1) Me.Name = "Form1"Me.Text = "Form1"Me.ResumeLayout(False) Me.PerformLayout() EndSubPublicSubNew() InitializeComponent() EndSubPrivateSub textbox_TextChanged(sender AsObject, e As EventArgs) Dim x__1 AsString = ""Dim X__2 AsString = ""EndSubEndClassEndNamespaceConversion Cases:
Case sensitive C# to VB:
The converter will automatically rename object if needed.
Event Handler C# to VB:
The event C# handler will be converted as follows:
C#:
this.textbox2.TextChanged += new System.EventHandler(this.textbox_TextChanged);VB:
AddHandlerMe.textbox2.TextChanged, New System.EventHandler(AddressOfMe.textbox_TextChanged)Why VB6 Upgrading is important:
Magic properties that make many programmer love VB6:
- Compile on demand: you could choose to make the source code code be complied at debug time on demand only.
- Edit and continue: In debug mode you not forced to restart your application after errors fix or code edit.
- Does not need dot net framework to run.
- COM and ole combatable.
VB 6.0 upgrading advantages
- Supporting 64 bit
- Faster running
- More resources
- Improve the maintenance of an application
- Increase developer productivity
VB 6.0 upgrading disadvantages
- Compile on demand will be lost.
- The resulting application need dot net farmworker will the original one is not
- If your application is a dynamic library; note that pre declared object is not supported in C# or VB.Net.
- If your application is ActiveX control or ActiveX Document then there is no acceptable converter for you; manual code rewriting is needed.
- The converter we save your time for converting but post conversion work is much needed.
What does pre declared object means:
I wrote a library in VB6 to be used as addin in Office VBA the user write following code when used my lib
Sub Test() IfNot NP.File.Exists("C:\Temp.txt") Then NP.File.Create "C:\Temp.txt" NP.File.Move "C:\Temp.txt", "C:\Temp2.txt" NP.File.Copy "C:\Temp2.txt", "C:\Temp.txt" NP.File.Delete "C:\Temp2.txt" NP.Shell "C:\Temp.txt"EndSubThe NP object is pre declared and no need to declare it in VBA In VB.Net Version of VBA Extend the user should add additional line The user should 1st declare an object named NP before using it.
Public NP AsNew VBAExtend.NP Sub Test() IfNot NP.File.Exists("C:\Temp.txt") Then NP.File.Create "C:\Temp.txt" NP.File.Move "C:\Temp.txt", "C:\Temp2.txt" NP.File.Copy "C:\Temp2.txt", "C:\Temp.txt" NP.File.Delete "C:\Temp2.txt" NP.Shell "C:\Temp.txt"EndSubBefore Converting:
- It is better to install VB6 but it is not a must
- Ensure that your application could be recompiled and run correctly.
- Ensure that all your referred library are available and work well in the current operating system.
- Make sure your code can be recompiled and run well before start converting.
- No convertors can grantee the 100% conversion.
- Make sure that the dot net language support your project type.
- Please note the VB6 converting is a hard work because of the programing language philosophy is defer VB6
VB6 Upgrade Companion VBUC:
- If you are familiar with upgrading VB6 then you will understand how useful this software.
- It safe too much of the upgrade time.
- In most time required many post conversion works.
- It is much better than the old upgrade engine that is included in versions 2003, 2005 and 2008 of VS
What VBUC can upgrade:
- Modules, Classes, Forms & MDIForms
- User Controls that used in the same project on in the same group
- Resource File
What VBUC can't upgrade:
- Property Page
- Designer files (*.Dsr)
- User Controls that used in web browser or ActiveX container
- ActiveX Document
Before Using VBUC:
The VBUC is feather software with many option and we should study before start converting:
- It is more simple to convert to VB.Net than C#.
- For ActiveX choose Com Visible
- Form options Use helper classes whenever it available
- For making you application more like .net designed use More dot net option
- If the above option fail use the More Automation options for less error in conversion.
- After converting complete open your project in VS and disable all warning and switch option explicit off and option strict off.
- If error is still appears try to fix them manually.
- Once you are able to compile your project try to follow warning
- Switch option explicit on and option strict on and follow any errors appears
VBUC Free version limitation:
It is work for project with less than 30,000 line code
VB Migration:
- New powerful VB6 converting application.
- If you are familiar with upgrading VB6 then you will understand how useful this software.
- It safe too much of the upgrade time.
- In most time required many post conversion works.
- It is much better than the old upgrade engine that is included in versions 2003, 2005 and 2008 of VS
- Its more simple and faster than VBUC
Properties
- Supports most major VB6 features
- Converting in trail software is done on the company server.
- Fast conversion of large project.
- .NET app will looks and behaves like the original VB6 code
- Simple interface
- Powerful supported libraries
- Integrated code editor
- staged migration is partial conversion is allowed
- Extendibility
- User control will be upgraded.
- Sub Main in DLL projects & Multi-threaded components
- Controls in VBMP’s support library expose properties and methods with same name as the original members, which ensures that code runs correctly even in late-bound scenarios
- Auto-implemented properties
What VB Migration can't upgrade
- Property Page
- Designer files (*.Dsr)
- User Controls that used in web browser or ActiveX container
- ActiveX Document
You can see Feature Comparison Table
Other VB6 upgrade links
Free PDF Printer
Works with Windows 10, 8.1, 8, 7, Vista, XP
and Windows Server 2016, 2012, 2008, 2003
Download
The Bullzip PDF Printer works as a Microsoft Windows printer and allows you to write PDF documents from virtually any Microsoft Windows application.
This program is FREEWARE with limitations, which means that there is a FREE version for personal and commercial use up to 10 users. It does not contain any advertising or popups. For commercial applications with more than 10 users there are commercial versions available with advanced features.
Features
- Print to PDF from almost any Windows program.
- Supports 64-bit operating systems.
- Direct output to the same file each time or prompt for destination.
- Control if the printer should ask if you want to see the resulting PDF document.
- Control output and prompts programmatically.
- Setup can run unattended.
- Graphical user interface.
- Password protect PDF documents.
- AES 256/128 bit encryption and standard 128/40 bit encryption.
- Quality settings (screen, printer, ebook, prepress).
- Set document properties.
- Watermark text, size, rotation, and transparency.
- Superimpose/background documents.
- Appending/prepending documents.
- User interface control.
- Linearized PDF documents for fast web view.
- PDF/A-1b support for long time storage of PDF documents.
- Signing of PDF documents using digital certificates.
- Command line interface to all settings.
- COM/ActiveX interface for programmatic control.
- Microsoft.NET API for C#, VB.NET, and other .NET development.
- Support for Citrix MetaFrame
- Support for Windows Terminal Server and RDP
- Multiple output types supported: BMP, JPEG, PCX, PDF, PNG, and TIFF.
- Upload document using FTP or SFTP protocol.
Download and Installation
The installation of this program is very simple. Just follow the few steps listed here:
- Download the latest stable PDF Printer (40.3 MB).
Go to download page - Run the setup program.
When the setup has completed you will have a printer called Bullzip PDF Printer. Now you are ready to print from your other applications.
During the installation it will check if you have all the components needed to run the software. If some of the required componets such as GPL Ghostscript are missing, it will suggest to download and install them for you.
Uninstall
If you later want to uninstall the program you can do so through the Add or Remove programs feature of Microsoft Windows.
MSI Package
If you want to have an MSI package for the setup program then we can recommend the enterprise edition or show you how to build you own customized MSI package for Windows Installer.
Translations
The users of this product have translated it to their local language. Below you can see the current status of the translations. If your language is incomplete or missing, you are welcome to help us translate the missing texts. more...
How-To Make a Translation
You can complete an existing translation or create a new translation.
- First you download the Excel file from the link below.
 Translations.zip
Translations.zip - Locate the column with the language that you want to complete. If your language is not listed then you just add a new column and write the name of your language. You don't have to fill in the rest of the codes in the green header fields. The information in those fields will be updated by us using our culture information.
- Create your translations in the selected column.
- Save and email the Excel file to . Please include a small description of what you have translated.
System Requirements
- Microsoft Windows Server 2016, 2012, 2008 R2, 2008, 2003, Windows 10, 8.1, 8, 7, XP
- GPL Ghostscript 9.10 or later
- Xpdf (optional)
- PDF Power Tool (optional)
Ghostscript is a free open source program that is able to convert PostScript to PDF files. It is distributed under the GNU General Public License. More information about Ghostscript is available here.
Download light weight Ghostscript distribution here (21.3 MB)
Download light weight Xpdf distribution here (1.0 MB)
Download PDF Power Tool (2.2 MB)
If you still run Windows NT 4.0 or Windows 2000, you can can find help in the short PDF Printer on Windows NT 4.0 or Windows 2000 guide.
License FAQ
Before you dive into the FAQ section you may want to take a quick look at the general license information.
Read more about the difference between Bullzip and bioPDF.
Video Training
You can find a couple of video guides at the Bullzip YouTube channel.
More Videos
One of our partners has supplied a free set of training videos for the Bullzip PDF Printer. Visit their web site to get access to the videos. 
PDF Studio
If you want to merge PDF files or rearrange pages then you should look at our PDF Studio program. With PDF Studio, you can
- Merge PDF files
- Rearrange pages
- Copy pages
- Delete pages
- View and search PDF files
- Command line PDF print
Version History
 Version history RSS Feed
Version history RSS Feed
2020-03-04 (11.13.0.2823)
- New <doccomputername> macro to get name of the originating computer in a shared printer installation.
- Fix for SFTP upload.
2020-02-09 (11.12.0.2816)
- Fix for Chrome version 80 postscript bug.
- Updated translations.
2019-12-03 (11.11.0.2804)
- Support for monitors with high DPI.
- Fix for start and end page when sending a PDF to a printer.
- Extended support for copy/paste of Chinese characters in PDF documents.
2019-07-11 (11.10.0.2761)
- New code for printing/redirecting the PDF to another printer.
- Compatibility with Ghostscript 9.27.
2019-02-17 (11.9.0.2735)
- Fixed overflow (error 6) problem.
- Support for setting signature on the last page.
- Updated translations.
2018-10-08 (11.8.0.2728)
- Added feature for remembering recent save locations.
- New setup command line switch ORIGINALDRIVER to keep the setup from changing the driver.
2018-05-06 (11.7.0.2716)
- Fixes setup issues.
- Updated translations.
2018-04-12 (11.6.0.2714)
- Select PDF/A-2b and PDF/A-3b from user interface.
- Fix for Word document creation on 64 bit systems.
- Resolution is now fixed to vectors when merging PDF background.
- Fix for installer on systems where WMI is not available.
- Updated translations.
2018-01-29 (11.5.0.2698)
- Open an email with the new PDF attached.
- Suppress errors when running in non interactive mode such as service accounts.
- More paper sizes in XPS mode.
- Updated translations.
2017-09-03 (11.4.0.2674)
- Abort print job if user in not interactive and dialogs should be shown.
- PrintToPrinter features fixed for running as a shared network printer.
- Fix for size of background PDF when running as a shared network printer.
2017-08-22 (11.3.0.2668)
- Updated translation for Portuguese (Brazil).
2017-08-20 (11.2.0.2667)
- Runonce configuration files are now picked up as soon as the spooler starts spooling print job to the printer port.
- User interface is now DPI aware. Fonts look nicer in different screen resolutions.
- Fix for running as a shared printer. Some print jobs looked different when coming from a shared printer.
- GUITimeout setting -1 problem fixed by keeping the document collector running until the GUI has finished processing the job.
- Support for XPS based printer drivers as an alternative to Postscript. This provides better Unicode support.
- Handles error where a configuration with an encrypted password is moved to another machine.
- Updated translations for Traditional Chinese, Greek, Russian, and Slovak
2017-03-10 (11.1.0.2600)
- Click on balloon notification to open PDF location.
- Trial message is now a link for more information.
- Unicode font support brought back to previous level.
2017-01-15 (11.0.0.2588)
- Document Collector program added to help merge documents.
- New
- Text extraction was improved.
- FIPS compliance detection added for new operating systems.
- GUITimeout defaults to 0 for better performance on multi user systems.
- Application crashes caused by DEVMODE structure was fixed.
2016-08-29 (10.25.0.2552)
- Shows an error if you are trying to use the program as a PDF reader.
- Shows license type on about page.
- Shows printer window in task bar.
- Defaults to 300 DPI instead of 600 DPI for smaller output files.
- New Merge function in API that supports font embedding.
- Updated translations.
2016-03-07 (10.24.0.2543)
- HTTP/HTTPS upload feature added.
- Security updates.
- Enhanced special character support in PDF passwords.
- New macro <outputpath> for the full path of the output file.
- New setting 'textfilename' to save the content of the print job as text.
- New setting 'textformat' controls if the text file is formatted as Unicode or UTF8.
- Fix for encryption of PDF versions lower than 1.4.
- Default GUI timeout was changed from 0 to 10 minutes for a better merging experience.
- New /NOTOOLS switch for the installer can skip all dependencies.
- VB Script macros now require the ALLOWEXECUTE flag to run when the macrodir setting is used.
- Fix for commercial distiller PPD to enhance compatibility.
- Fix for job names on printer queue when sending output to another printer.
- Installs on Windows Server 2016 Preview 4.
- Updated translations.
2015-09-28 (10.23.0.2529)
2015-09-15 (10.22.0.2525)
- User interface load time performance improvements.
- Updated translations.
2015-09-03 (10.21.0.2462)
- Another false positive detection in Norton AV and Symantech EndPoint.
2015-08-31 (10.20.0.2459)
- Fix for a false positive detection in Norton AV.
2015-08-27 (10.19.0.2457)
- Microsoft.NET API encryption changed to support Dynamics NAV server on Windows 10.
2015-08-25 (10.18.0.2455)
- Performance improvements to compensate for changes in Microsoft Security Essentials and EndPoint.
- Ignore empty registry settings.
- Updated translations.
2015-08-23 (10.17.0.2428)
- Another false positive virus detection removed.
2015-08-21 (10.16.0.2426)
- Uninstallation of Xpdf fixed.
- False positive virus detection removed.
2015-08-19 (10.15.0.2424)
2015-08-19 (10.14.0.2421)
- Create Microsoft Word documents from print jobs.
- New function GetWindowsDefaultPrinterName in PdfUtil API assembly.
- Support for commercial distiller on file systems without short names.
- Experimental support for PDF/A-3b format.
- Fixes file time stamp for attached files.
- Print to printer after output is created.
- AllowExecute setting added to the registry to improve security.
2015-06-16 (10.13.0.2368)
- Fix for uninstalling program specific event log.
2015-05-12 (10.12.0.2363)
2015-05-11 (10.12.0.2361)
- Fix to disable image compression with commercial distiller.
- Commercial distiller now uses Flate image compression by default.
- New image compression settings (ImageCompressionLevel, ImageCompressionType, ImageCompressionQuality) for commercial distiller.
- PrinterName context variable added for VBS macros.
- Fixes problem with save as dialog selection being lost.
- Fix for Korean Unicode license decoding.
2015-03-18 (10.11.0.2338)
- New smarttitlefind and smarttitlereplace settings to control file name suggestion.
- New
- New setup command line switch USEDOTNET20 to force the use of Microsoft.NET 2.0.
- Remember last used option set with support for hidden dialogs.
- Fixes for systems without support for 8.3 file name creation.
- Escaping of characters fixed for job specific runonce file naming.
- COM API method Merge2 added to supported merging from VB Script.
- Improved support for file names with regional characters in the Merge function.
- Write status file if AfterPrintProgram or RunOnError fails.
- Updated translations: Swedish, Slovenian, Urdu
2014-12-02 (10.10.0.2307)
- Handles PostScript jobs larger than 2GB.
- New hideoptiontabs setting to control which tabs are visible in the options dialog.
- Fix for hiding run action error dialog in silent mode.
2014-11-11 (10.9.0.2300)
- Works with Windows 10 Technical Preview.
- Improvements for non-interactive users.
- New installer switch: PostScriptLanguageLevel to control the language level of the driver.
- New installer switch: PostScriptOutputOption to control the output options of the driver.
- New installer switch: DPI to control the default resolution of the driver.
- New installer switch: AdvancedFeatures to enable or disable the advanced features of the PostScript driver.
2014-09-03 (10.8.0.2282)
- Fix of possible deadlock when reading error output from programs.
- New /SPOOLERCONTEXT setup command line switch for easier installation with services such as IIS.
- Advanced features of Postscript driver were disabled to fix left to right (LTR) printing issues.
- Registration of msscript.ocx during installation was moved to 64-bit context when possible to avoid access error (0x5) problems.
2014-08-01 (10.7.0.2277)
- Fixes problems with detection of installed Ghostscript.
- New ICC profile for better PDF/A compatibility.
- Support for different PDF versions in PDF/A creation.
- Now uses ps2write device for PostScript generation with Ghostscript.
- More paper sizes added.
- Translation updates: Polish, Slovak.
2014-05-17 (10.6.0.2267)
- Support for Ghostscript 9.14 (32-bit and 64-bit).
- Fixes installation error: Operation could not be completed (error 0x00000704). The specified port is unknown.
2014-05-06 (10.5.0.2262)
- FIPS compliant. Works with United States Federal Information Processing Standard (FIPS) validation enabled.
- AES 128 bit encryption is now supported with the commercial distiller.
- Support for
- New macro tags: <printername>, <commonapplicationdata>, and <localapplicationdata>.
- New /SHARE switch for the setup program to enable network sharing on print servers.
- Improved port monitor reports errors to the event log.
- Fixed copying sample configuration files for custom printer names.
2014-03-21 (10.4.0.2240)
- Context menus now support Unicode.
- New LicenseData setting to hold a base64 encoded license string.
- New IgnoreCopies setting to make only one copy of a document in the PDF instead of the specified number in the print job.
- New FastTrack setting for fast image creation. Many features are ignored in fast track mode.
- New Producer setting to set PDF Producer property.
- New Creator setting to set Application property in the PDF.
- Font compression enabled for PDF/A to reduce file size.
- Default PDF/A color space changed to RGB.
- Administrators can now use the printer on a remote connection without a professional license.
- Supports hard coded license levels in redistribution builds.
2014-02-18 (10.3.0.2191)
- New PDF command line tool for merging and printing PDF documents.
- Fix for temporary paths with Unicode characters.
- Fix for systems with multiple copies of the same font.
- Fix for not remembering the last output device.
- Commercial distiller uses standard encoded fonts.
- Install option to override default TrueTypeDownload setting.
- Produces smaller PDF/A documents.
- Performance tuning through GSGarbageCollection setting.
2014-01-09 (10.2.0.2141)
- Toolbar removed from free version.
- Improved color support in PDF/A-1b documents.
- New setting to change the ICC profile for smaller PDF/A-1b documents.
- Option dialog now supports FTP, and SFTP uploads.
- Option dialog now supports running programs on success and error.
- Option dialog now supports running program after processing a print job.
- Default RunOnSuccessMode, RunOnErrorMode, and AfterprintProgramMode changed from Hide to Normal.
- New API method to print PDF documents to a specific Windows printer.
- New support for AES 128 and AES 256 bit encryption of PDF documents.
- New setting to control confirmations of folder creation.
- Advanced option dialog with buttons to edit global.ini, print a test page, and more.
- New options dialog tabs for file upload, running programs, and signing with digital certificates.
- Supported Ghostscript version is now 9.10 or later.
- Supported PDF Power Tool version is now 3.0.0.6 or later.
- Improved Unicode support.
- Belarusian translation added.
2013-10-08 (10.1.0.1871)
- New pagecount macro that inserts the number of pages in the print job.
- New experimental PdfUtil.PrintPdf function in API.
- More Unicode stuff.
2013-09-26 (10.0.0.1840)
- Greatly enhanced Unicode support in user interface.
- New settings to upload the result to FTP or SFTP servers.
- One MSI package for both silent and non-silent installation.
- Does not set the installed printer as default unless no default printer was selected by the user.
- Additional registry cleanup in uninstaller.
- Cleanup of failed print jobs.
- Support for Ghostscript 9.10.
- Color model setting to force RBB, CMYK, or Grayscale.
- Updated translations.
- Support Windows 2000 was discontinued.
2013-07-30 (9.10.0.1629)
- Support for Windows 8.1 Preview.
- Image compression is turned on by default.
- Image compression setting can be changed from the user interface.
- Digitally sign PDF files using certificates in the certificate store.
- New settings: SignThumbprint, SignStoreName, and SignStoreLocation.
- Improved uninstall routine for cleaner uninstall.
2013-07-15 (9.9.0.1621)
- Image compression is turned off by default for better quality.
- New setting 'imagecompression=yes|no' added to control image compression.
- GUI encrypts owner and user passwords in configuration files.
- Path to status file can now be passed as %4 to programs used in 'AfterPrintProgram', 'RunOnSuccess', and 'RunOnError'.
- Default ICC color profile was changed for PDF/A-1b compatibility.
2013-04-19 (9.8.0.1599)
- Improved setup for Windows XP machines.
- Fixes loading of option sets with different device settings.
2013-03-28 (9.7.0.1592)
- More robust installer that handles problem when HP drivers are not installing correctly (error 0x00000002).
- Additional GUI improvements and localization.
2013-02-25 (9.6.0.1582)
- More improvements for the sponsor offer screen to clarify the options.
2013-02-20 (9.5.0.1579)
- Fix in the sponsor offer screen to make it more clear how not to install the offer.
- Minor layout issues with high screen DPI settings fixed.
2013-02-19 (9.4.0.1570)
- Improved quality and file size in superimpose operations.
- Locates Xpdf and Ghostscript Lite packs outside the printer's application folder.
- Much improved MSI files for distribution via Group Policy Objects.
- MSI package changed to preserve the default printer and suppress message boxes.
- Bug Radar removed from Windows 8 Start Menu.
- Product split in three different versions (free, pro, and enterprise).
- AVG sponsors the free download with an optional offering.
2012-12-05 (9.3.0.1516)
- Change user interface language for specific users.
- Support for PDF compatibility level 1.7.
- New <counter> macro.
- New <ticks> macro.
- New <now> macro.
- Shell execute mode support for RunOnSuccess, RunOnError, and AfterPrintProgram.
2012-11-05 (9.2.0.1499)
- Max size of custom pages was increased to 1000 by 1000 inches.
- Built using Visual Studio 2012.
- OwnerPassword and UserPassword settings now support macros.
- New macro
- New macro
- Support for attaching files inside the PDF document.
2012-10-09 (9.1.0.1454)
- New PrinterVersion property in PdfSettings API.
- Silent MSI package.
2012-09-21 (9.0.0.1437)
- Support for Windows Server 2012.
- Support for Windwos 8 RTM was added.
- Support for Windows 8 Consumer Preview was removed.
- Print from Metro style applications in Windwos 8.
- New /SourceDir setup prarameter.
2012-08-30 (8.4.0.1425)
- Improved embedding of fonts.
- Register assemblies for use with Visual Studio 2010.
- Samples of global.ini, defaults.ini, and settings.ini are installed.
- Changes in license file.
- Print encrypted documents.
2012-04-10 (8.2.0.1406)
- New settings EmbedAllFonts and SubsetFonts.
- Writes a job.ini file with print job information in the printer's temp folder.
2012-03-06 (8.2.0.1394)
- Support for Windows 8 Consumer Preview 32 bit (x86).
- Support for Windows 8 Consumer Preview 64 bit (x64).
- Discontinued support for Windows 8 Developer Preview.
- Commercial version without Ghostscript dependency available on request.
- Internal API functions isolated in PdfInternal interface.
- Improved uninstaller.
- Updated translations.
- Minor tweaks.
2012-01-02 (7.2.0.1338)
- Support for both Microsoft.NET Framework 2.0 and 4.0.
- Updated translations.
- Minor tweaks.
2011-09-27 (7.2.0.1320)
- Works with Windows 8 (Developers Preview).
- Support for Microsoft.NET Framework 4.
2011-09-15 (7.2.0.1319)
- Fix for writing configuration files.
2011-09-14 (7.2.0.1317)
- GSLite updated to version 9.04.
- Updated translations.
2011-08-17 (7.2.0.1313)
- Control the priority class of the PDF processes.
- Limited support for PStill converter was added.
- Debugging feature named BugRadar was added.
2011-04-07 (7.2.0.1304)
- Minor fixes since the beta version 7.2.0.1288
- Modifications in the parameter exchange with customized GUI.
- CustomGui setting now holds a command line instead of only the executable.
- Many translations were updated.
2011-02-23 (7.2.0.1288)
- You will now get multiple copies of the document inside the same PDF if you set the number of copies in the printing dialog.
- Now supports re-distilling of encrypted PDF documents. This requires that you are the owner of the content.
- Multiple option sets can now be defined. This enables you to select between sets of preconfigured settings when you create your PDF documents.
- Append to the output file if it already exists.
- Support for 64 bit Ghostscript 9.01.
- Better cleanup during uninstall.
- Advanced customization feature where you can replace the GUI with your own executable file made in your favorite programming language.
- Fix for background syntax. There was a problem with the notation such as <F1> when used together with the pdftk.exe
2010-09-28 (7.1.0.1218)
- Support for Ghostscript 9.00
- Fix for runtime error 438 when the file name field in settings.ini is empty.
- Support for custom license agreements.
2010-09-18 (7.1.0.1212)
- New MacroScriptTimeout setting to control the script timeout when running VB Script macros.
- New MacroAllowUI setting to control the display of message boxes when running VB Script macros.
- New context value AppPath when running VB Script macros.
- Support for pdftk in superimpose operations.
- Lists only local printers when running the options dialog. Mapped printers are not shown in Citrix and Terminal Server sessions.
- Macros can abort the process by setting the Abort to true in the context dictionary.
- Scripting engine is only initialized if macro files are present.
- Updated translations (Arabic, Bosnian, Bulgarian, Dutch, Hebrew, Hungarian, Kannada, Lithuanian, Slovak)
2010-05-30 (7.1.0.1195)
- RunOnError registry setting added for error handling by the printer port.
- TempFolder registry setting added for control of temporary folder for the printer port.
2010-05-11 (7.1.0.1186)
- Smarttitle macro updated to filter out the [Compatibility Mode] tag in Microsoft Office.
- New registry settings 'Disable Impersonation', 'Application Data', 'Common Application Data' and 'Local Application Data' were added to improve printing from IIS and sharing the printer on the network.
- Malay language was added.
- Updated translations (Czech, Arabic, Japanese, Russian, Ukrainian, Turkish, Spanish, Catalan, Korean)
2010-03-21 (7.1.0.1181)
- New job specific runonce files of the form runonce_documentname.ini.
- Forces that error meszsages are suppressed when the user is a service account ending with a $ sign.
- New runonce command line parameter for gui.exe to force the use of a specific runonce settings file.
- New context variables for Visual Basic Scripting (DocumentName, DocumentAuthor, DocumentCreationDate)
- Updated translations (Estonian, Romanian)
2010-03-08 (7.1.0.1159)
- Fix: Option dialog reported a runtime error 91 when closed.
2010-03-07 (7.1.0.1157)
- New macro context variables ErrorNumber, ErrorDescription, and ErrorSource.
- New settings RunOnSuccessMode, RunOnErrorMode, and AfterPrintProgramMode.
- New setup command line switches GSLiteURL and GSLiteDownloadMode.
- Registers .NET API for use in Visual Studio 2008.
- Fix: The RunOnError command line is now executed if a macro raises an error.
- Fix: Both OnSuccess and OnError event handlers fired on error and success.
- Fix: RunOnErrorDir was ignored and the RunOnError was set as default dir.
- Updated translations (Swedish, Norwegian, Dutch, Afrikaans, Spanish, Finnish, Croatian, German, Portuguese - Brazil, Portuguese - Portugal, Greek, Slovenian, Indonesian, Polish, French, Turkish, Chinese - simplified, Chinese - traditional, Italian).
2010-02-08 (7.1.0.1140)
- New <app> macro added to represent the application folder where gui.exe is installed.
- Fix of error when output format is different from PDF and encryption was enabled.
- Fix of problem with the Save As dialog.
- Updated translations (Norwegian, Finnish, British English, Australian English, Lithuanian).
2010-01-18 (7.1.0.1136)
- New wipemethod=3pass setting is now supported to do a 3 pass wipe of temporary files created during PDF or image creation.
- Settings RunOnSuccess, RunOnSuccessDir, RunOnError, RunOnErrorDir, AfterPrintProgram, AfterPrintProgramDir and StatusFile now support macro substitution.
- Fix for reading Unicode postscript properties written using octal numbers on Windows 2000.
- Fix for missing text on buttons on Windows 2000.
- Fix for selecting the correct file extension when using the Save As dialog.
- Problem where the installer reported "Not implemented" has been fixed.
- Updated translations (Croatian, Hebrew, Thai, Turkish, Romanian, Greek).
2009-12-25 (7.1.0.1082)
- Fix of error 429 when using ActiveX object 'BioPdf.PdfWriter.Xmp' on 64 bit systems.
- Updated translations (Brazilian Portuguese, Slovenian, Ukrainian, British English, Australian English, Polish, Japanese).
2009-12-12 (7.1.0.1080)
- Digitally signed setup program.
- Updated translations (Hungarian, Traditional Chinese, Simplified Chinese, Russian, Portuguese, Swedish, German, Spanish, Italian, Serbian).
2009-11-29 (7.1.0.1078)
- Improved handling of Unicode in GUI.
- Support for Ghostscript 8.70.
- New feature: Create linearized PDF files for optimized web viewing.
- Fix: Patching PDFA XMP data structure when using non western code pages.
- New feature: Show list of page thumb nail images when opening the PDF.
- Fixed Thai translation.
- Updated translations (Hungarian, Estonian, Finnish, Arabic, Traditional Chinese, Greek, Catalan, Turkish).
2009-11-10 (7.1.0.1007)
- Improved handling of Unicode document titles.
- Allows appending with the same file name as the output even if the append file doesn't exist.
- GUI.EXE parameter names are no longer case sensitive.
- Advanced printer setting 'ICM Method' now defaults to 'ICM Disabled'.
- Advanced printer setting 'TrueType Font Download Option' now defaults to 'Outline'.
- New setup command line switch /PRESERVEDEFAULTPRINTER.
- The user's advanced settings are now reset during installation.
- Setup will default to paper size A4 unless the locale indicates USA or Canada.
- Setup can now distribute content to the special folders 'Application Data', 'Common Application Data', and 'Local Application Data'.
- Non translated setup messages will be shown in English instead of showing up as blank.
- Color problem when printing red on Windows XP has been fixed.
- Added translation (Thai).
- Updated translations (Japanese, Afrikaans, German, Hebrew, Slovak, Swedish, Dutch, Russian, Danish, Bulgarian, Norwegian, Brazilian Portuguese, Simplified Chinese, Slovenian).
2009-10-09 (7.0.0.928)
- Setup detects if gslite.exe is outdated.
- Fix: Encoding of setup texts fixes the display of garbage.
- Unicode output file names support when running witout GUI.
- Unicode messages supported.
- Updated translations (Czech, French, Italian, Japanese, Polish, Spanish).
2009-10-01 (7.0.0.926)
- Official support for Windows 7.
- Microsoft.NET API was introduced.
- Ini files settings.ini, runonce.ini, global.ini, defaults.ini, and user.ini have changed location.
- Ini files no longer have the printer name in their file name.
- Status file now supports Unicode and UTF-8 encoding with descriptors.
- MessageCode and MessageText added in the status file.
- Better support for Unicode in PDF/A XMP structure.
- Auto detect Unicode or UTF-8 encoding of ini files.
- The use of cmd /c for starting external programs was removed to allow command lines containing & and other special chars
- Improvement of the smarttitle macro. It now removes additional Microsoft Office extensions.
- Australian English language was added.
- UK English language was added.
- Farsi language was added.
- Other translations were updated.
2009-05-04 (6.0.0.865)
- Experimental support for PDF/A-1b document standard.
- New setting 'icc' to specify color profile for PDF/A creation.
- New setting 'format' is used to specify pdfa1b when creating PDF/A-1b documents.
- New setting 'AutoRotatePages' to control automatic page orientation.
- New setting 'Orientation' to control fixed page orientation.
- New /PreserveDefaultPrinter command line switch for the setup program.
- Hindi language was added.
- Requires latest gslite 8.64 or full Ghostscript 8.64 or later.
2009-02-22 (6.0.0.766)
- Support for Adobe Normalizer as document converter instead of Ghostscript.
- Merge operation allows Postscript files as input in addition to PDF files.
- Superimpose operation allows Encapsulated Postscript as input in addition to PDF files.
- Postscript added as output type. New devices are pswrite and psraw.
- A new file name macro <smarttitle> was added to remove strings like "Microsoft Word -" from the document title.
- Translation updates.
2009-01-26 (6.0.0.744)
- New gslite.exe distribution to fix performance problems on Citrix installations where the C drive is a mapped client drive.
- Translation updates.
2009-01-13 (6.0.0.741)
- Experimental support for Windows 7 beta.
- Fix for problem with creating folders on UNC paths.
- Translation updates (Swedish, Norwegian).
2008-12-24 (6.0.0.728)
- Error when saving a document to the root folder of a drive has been fixed.
2008-12-20 (6.0.0.725)
- New defaults.ini file introduced to override default values.
- Creates output folder if it doesn't exist.
- Ignores missing merge files when controlled via runonce.ini.
- If Scripting is not available then all VB Script macros will result in an empty string.
- New Esperanto translation.
- Translation updates (Afrikaans, Croatian, Estonian, Hebrew, Slovak, Turkish).
2008-11-01 (6.0.0.702)
- The Save As dialog now selects the output format based on the file name extension.
- Implementation of the DeviceList setting was improved.
- Problem with diagonal strange black dots should be solved.
- Translation updates (Traditional Chinese, Ukrainian, Dutch, Vietnamese, Latvian).
2008-10-21 (6.0.0.695)
- VBScript macros and events are now supported. This extends the programmatic control you have over the PDF Writer.
- New setting: LicenseFile. With this setting you can specify which license to use. This feature is meant for a redistribution scenario.
- New setting: MacroDir. This controls where the VBScript macros and event handlers are loaded from.
- New setting: ExtractText. The printer can now extract text information from the print job. This text can be parsed and values can be extracted and used as macros such as author or title.
- Translation updates (Estonian, Simplified Chinese, Spanish, Finnish).
2008-09-26 (6.0.0.690)
- Multi merge feature released. more...
- Translation updates (Italian, Romanian, Bulgarian, Swedish, French, Slovenian, Czech).
2008-09-19 (6.0.0.684-5)
- Translation updates (Brazilian Portuguese, Hungarian, Simplified Chinese).
2008-09-18 (6.0.0.684-4)
- Translation updates (Russian, Japanese, Portuguese).
2008-09-16 (6.0.0.684-3)
- Translation updates (Serbian, Polish).
2008-09-16 (6.0.0.684-2)
- Translation updates (Italian, Spanish, Portuguese).
2008-09-15 (6.0.0.684)
- ConfirmOverwrite setting is now supported in unattended mode. Use ConfirmOverwrite=no if you want to overwrite the destination file without a prompt.
- Translation updates (Russian).
2008-09-14 (6.0.0.679)
- Avoid detection as a virus for F-Secure users.
- Fix in config.exe to allow mixed case parameter values.
- Translation updates (Catalan).
2008-09-05 (6.0.0.664)
- Driver settings USERTEMP and USERDATA are no longer supported.
- Improvements for PDF Printer redistribution and customization.
- Installation and unstallation now supports multiple instances of the program installed on the same computer.
- Registry value HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE \ SYSTEM \ CurrentControlSet \ Control \ Print \ Printers \ Bullzip PDF Printer \ AppFolder is now written to associate the installed printer with a specific program folder.
- Uninstall only removes printers where the AppFolder registry value matches the application folder being uninstalled.
- /NOHOMEPAGEICON command line switch for the setup program. The home page icon will not be installed in the start menu when this parameter is specified.
- Translation updates (Estonian, Vietnamese)
- Registry value HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE \ SOFTWARE \ Bullzip \ PDF Printer \ Settings \ GhostscriptFolder is no longer added by the setup program when it installs Ghostscript.
2008-08-10 (6.0.0.659)
- New compatibilitylevel setting. It will control the PDF compatibility level. Valid values are 1.1, 1.2, 1.3, 1.4, and 1.5. This setting can also be controlled from the GUI.
- Support for the <pageno> macro in the PDF output file name. This will split the resulting PDF document into one file per page.
- Updated translations.
2008-07-18 (6.0.0.648)
- Superimpose on top of printout is now supported. With this you can superimpose on print jobs from Internet Explorer and Firefox.
- Tab order fixed.
- Setup customization through setup.ini.
- Multiple printers can be installed using the /PRINTERNAME="Printer1,Printer2" setup command line switch.
2008-07-14 (6.0.0.641)
- Major version changed from 5 to 6.
- Freeware license was limited to 10 users.
- Dependency on the Microsoft Scripting Dictionary component was removed.
- Better support for Adobe PageMaker. Use "general" PPD setting in printing dialog.
- More image formats are now supported (BMP, JPEG, PCX, PDF, PNG, TIFF).
- GUI now supports creation of image formats.
- Resolution can be specified for background PDF documents in superimpose operation.
- <desktop> macro was changed from special folder CSIDL_DESKTOP to CSIDL_DESKTOPDIRECTORY.
2008-05-13 (5.0.0.609)
- Correction of "Error 53: File not found" during cleanup in temporary files.
- Fix of problem with strange characters overlaying the finished PDF document.
2008-05-06 (5.0.0.599)
- Multiple /PRINTERNAME can be specified during setup to install more than one printer. (* only available in custom builds and bioPDF PDF Writer)
- Uninstall will remove all printers attached to the uninstalled port.
- Dialog control identifiers have been modified to support hiding and disabling.
- If no global@printername.ini file is found it will fall back to search for global.ini.
- Translations added (Norwegian - nynorsk).
- Translations updated (Norwegian - bokmål).
2008-04-20 (5.0.0.594)
- Translations added (Bosnian, Slovenian).
- Translations updated (Polish, Italian).
2008-04-09 (5.0.0.590)
- Ini files are now coupled to the printer name. Ex. settings@MyPDFCreator.ini will hold settings for a printer named MyPDFCreator.
- Contents of an App folder placed next to the setup program is copied to the program folder during installation. (* only available in custom builds and bioPDF PDF Writer)
2008-03-27 (4.0.0.575)
- Problem with ini files written as Unicode has been fixed. The problem was introduced in version 4.0.0.564.
- AfterPrintProgram is now run in case of success. This was disabled by a programming error.
2008-03-26 (4.0.0.570)
- New experimental settings (hidetabs, hidecontrols, disablecontrols).
- Translations updated (Korean).
2008-03-21 (4.0.0.568)
- Version number is written to printer comment field during installation.
- Translations updated (Arabic, Greek, Portuguese-Brazil).
2008-03-13 (4.0.0.564)
- Support for programmatic creation of JPEG, TIFF, and PNG image files instead of PDF documents.
- New settings: res, resx, resy, textalphabits, graphicsalphabits, device, and statusfile.
2008-03-03 (4.0.0.549)
- Translations updated (Spanish, Slovak).
2008-02-21 (4.0.0.545)
- Translations added (Ukrainian, Korean).
- Problem with installing olepro32.dll on Vista should be fixed.
2008-02-12 (4.0.0.543)
- "Save As" dialog shows in front of the printing application in Windows Vista.
- Translations updated (Afrikaans, Russian).
2008-02-04 (4.0.0.485)
- /PAPERSIZE installation switch added.
- Translations updated (Czech, Finnish, Galician, Simplified Chinese).
- Registration of comdlg32.ocx changed to avoid launching other Windows Installers.
2008-01-21 (4.0.0.463-7)
- Translations updated (Norwegian, Traditional Chinese).
2008-01-20 (4.0.0.463-6)
- Translations updated (Dutch, Indonesian, Polish).
2008-01-16 (4.0.0.463-5)
- Translations updated (Hebrew, Japanese, Portuguese).
2008-01-15 (4.0.0.463-4)
- Translations updated (Turkish, Latvian).
2008-01-14 (4.0.0.463-3)
2008-01-13 (4.0.0.463-2)
2008-01-09 (4.0.0.463)
- Bulgarian translation completed.
- Swedish translation completed.
- Portuguese (Brazil) translation completed.
- Polish translation completed.
- Japanese translation completed.
- Hungarian translation completed.
- Catalan translation completed.
- Bulgarian translation completed.
2008-01-05 (4.0.0.462)
- German translation completed.
2007-12-30 (4.0.0.459)
- Error 53 when merging with other documents has been fixed.
2007-12-17 (4.0.0.456)
- Automatic download and installation of Ghostscript Lite distribution.
- Progress indicator is now shown it the system tray.
- Balloon tip notification when the PDF is created.
- More work done on the Visual Basic Script macros.
- New settings supported: showprogress, showprogressfinished, runonerror, runonerrordir, runonsuccess, and runonsuccessdir.
- Fix: Earlier versions could sometimes remove custom defined paper sizes for other printers during installation.
2007-11-26 (4.0.0.432)
- Watermarks now use TrueType fonts instead of Ghostscript fonts.
- Requires Ghostscript 8.50 or later.
- Runtime error 380 should no longer occur during startup.
2007-11-21 (4.0.0.419)
- Fix for dialog sizes on remote desktop connections.
2007-11-19 (4.0.0.412)
- The settings UseDefaultAuthor and UseDefaultTitle now defaults to no.
- Security, Zoom, and UseThumbs settings now also work when merging documents.
2007-11-14 (4.0.0.408)
- New Feature: Remember last used folder name.
- New Feature: Remember last used file name.
- New Feature: PDF Watermarks/stamps can now be placed both over and under the normal print. This enables the use of PDF stamping the PDF files.
- New Feature: PDF Watermarks/stamps can use different colors, fonts and outline style.
- New Feature: PDF Watermarks/stamps can be placed anywhere on the page.
- New Feature: Open destination folder after PDF creation.
- Setting watermarksize is now obsolete use watermarkfontsize instead.
- Setting watermarktransparency is now obsolete use watermarkcolor instead.
- By default the watermark will now behave as a stamp and be placed on top of the print.
- Setting suppresserrors is default set to no.
- Setting usedefaultauthor is default set to yes.
- Setting usedefaulttitle is default set to yes.
- New setting watermarkcolor is now supported.
- New setting watermarkfontname is now supported.
- New setting watermarkfontsize is now supported.
- New setting watermarkoutlinewidth is now supported.
- New setting watermarklayer is now supported.
- New setting watermarkverticalposition is now supported.
- New setting watermarkhorizontalposition is now supported.
- New setting watermarkverticaladjustment is now supported.
- New setting watermarkhorizontaladjustment is now supported.
- New setting rememberlastfilename is now supported.
- New setting rememberlastfoldername is now supported.
- New setting zoom is now supported by the user interface.
- User's current selection of folder and file name are now saved in user.ini.
- Japanese language added.
2007-10-14 (3.0.0.352)
- Supports printing in Window Vista Internet Explorer running in protected mode.
- Slovak language added.
2007-10-07 (3.0.0.332)
- Improved memory handling when printing large documents.
- New Zoom setting to determine the initial zoom factor when a document is viewed.
- New UseThumbs setting to show thumbnail pictures of pages when a document is viewed.
- Polish language added.
2007-09-26 (3.0.0.323)
- Discards abandoned jobs for improved stability on Citrix.
- Override port log file folder with registry setting.
- Support for debug mode in print monitor.
- Monitor removes postscript file if the job is discarded.
2007-08-24 (3.0.0.313)
- Fix: Uninstall no longer removes additional printers.
2007-08-23 (3.0.0.310)
- Fix: Setup program of version 3.0.0.309 was not compressed.
2007-08-23 (3.0.0.309)
- Specific background images for all pages. more...
- Instances are now recognized by the options dialog.
- UNC roots are now valid destinations.
- Arabic added as new language.
2007-08-09 (3.0.0.290)
- Experimental support for named instances of the printer. This allows installation of multiple printers running with different settings.
2007-07-28 (3.0.0.278)
- Support for file systems without support for 8.3 representation of long file names. Fixes problems in some Vista installations.
- Problems with installing msxml6.dll have been fixed.
2007-07-25 (3.0.0.275)
- Improvements to Citrix installation to avoid the "The arguments are invalid" message.
- Dependency of Scripting.FileSystemObject has been removed.
- Improved encoding of the PDF property values such as title and author.
- Greek added as new language.
- Serbian added as new language.
- Swedish added as new language.
2007-07-05 (3.0.0.270)
- Retries moving destination file if it is locked by Antivirus software for some time after generation.
- <basedocname> macro no longer contains the directory part.
- Introduction of global.ini.
- New GhostscriptTimeout setting in configuration files.
- New AfterPrintProgram setting in configuration files.
- New AfterPrintProgramDir setting in configuration files.
- New DisableOptionDialog setting in configuration files.
- PDF compatibility level changed from 1.4 to 1.6.
2007-06-04 (3.0.0.222)
- Printing dialog now captures focus on Windows Vista.
2007-06-01 (3.0.0.215)
- Forces target settings to lower case. This is done to make the programming interface more robust to mixed case in the target settings.
2007-05-28 (3.0.0.211)
- Italian added as new language.
2007-05-22 (3.0.0.210)
- Spanish added as new language.
- Simplified Chinese as new language.
- Traditional Chinese as new language.
2007-05-18 (3.0.0.209)
- Use of /NOICONS during silent install will not install icons in start menu, desktop, and quick launch.
- Support for Scandinavian characters in watermarks.
- Additional architectural paper sizes ARCH E1 and ARCH E1 Half.
- Turkish added as new language.
2007-05-08 (3.0.0.201)
- New printer driver (PPD file)
- More paper types supported (Letter, Ledger, Legal, A3, A4, A5, 11x17, Note, A2, A6, LetterSmall, A0, A1, A4Small, A7, A8, A9, A10, ISO B0, ISO B1, ISO B2, ISO B3, ISO B4, ISO B5, ISO B6, JIS B0, JIS B1, JIS B2, JIS B3, JIS B4, JIS B5, JIS , 6, C0, C1, C2, C3, C4, C5, C6, ARCHE, ARCHD, ARCHC, ARCHB, ARCHA, FLSA, FLSE, HalfLetter, PA4, and Custom Page Sizes)
- Specify PDF Settings (color model, image compression, compatibility, auto rotate pages, embedded fonts, subset fonts, and page compression)
- Placing a file named debug.txt in the program folder will set the program in debug mode.
- Russian and Hungarian added as new languages.
2007-04-11 (3.0.0.186)
- Fix: Error message removed when installing on XP 64 bit.
- Fix: Specifying folders as default file names has been improved.
2007-04-09 (3.0.0.181)
- Fix: Maximize button disabled in options dialog.
- Fix: Minor change in watermark routine.
2007-04-09 (3.0.0.174)
- The printer has been localized to Portuguese (Brazil).
- Improvement: The output setting can be used to specify a default folder.
2007-03-25 (3.0.0.164)
- The printer has been localized to German and Danish.
- /noghostscript parameter for setup program will skip the check for Ghostscript.
- Fix: Open PDF documents after printing.
2007-02-28 (3.0.0.133)
- Fix: Removed dependency for Windows Scripting Host version 5.5.
- Fix: Spelling errors.
- Fix: In the previous version some jobs would lock the print spooler queue. This has now been fixed.
2007-02-20 (3.0.0.129)
- Feature: The config.exe utility now supports /C that will remove all settings.
- Fix: Merging with a file that doesn't exist does no longer create an empty PDF file.
- Fix: The previous version could only detect Ghostscript 8.54.
- Fix: The config.exe utility reported an error when setting values.
2007-02-12 (3.0.0.125)
- Fix in detection of 32-bit Ghostscript on x64 systems.
2007-02-12 (3.0.0.122)
- Fix in detection of Ghostscript on x64 systems.
- Extra error handling added.
2007-02-10 (3.0.0.25)
- No compatibility with older versions!
- Graphical user interface added.
- Major rewrite of the printer driver.
- Support for Citrix MetaFrame.
- Support for Windows Terminal Server.
- COM/ActiveX interface for programmatic control was added.
- Improved setup program.
2006-12-11 (2.0.0.24)
2006-12-07 (2.0.0.23)
- Support for Windows Vista x64 (64 bit edition).
- Support for Windows 2003 x64 (64 bit edition).
- New Feature: <basedocname> macro added for the Output setting.
2006-12-03 (2.0.0.22)
- Support for Windows Vista.
- Shows messages and SaveAs dialogs in the user's context. In theory this should improve the support on Terminal Server and Citrix. However, it has not been tested.
- New Feature: The output name in the settings.ini can contain macro names such as <docname> and <date>, which will be substituted with the actual document name and current date when the PDF document is generated.
- Misc. fixes.
2006-09-22 (1.0.0.20)
- Fix: Reads Author, CreationDate, Creator, Keywords, ModDate, Subject, Target and Title form settings.ini.
2006-08-28 (1.0.0.19)
- New Feature: Output quality control.
- New Feature: 40 bit and 128 bit password encryption.
- New Feature: Access permissions.
- New Feature: Watermarks.
- New Feature: Superimpose PDF documents.
- New Feature: Set document properties.
- Fixes in the printer driver.
- Setup program improved to solve problems on Windows XP Home.
2006-05-13 (1.0.0.18)
- The printer driver now works with all Ghostscript 8.x versions.
2006-01-25 (1.0.0.17)
- Users no longer need admin privileges in order to use the printer driver.
- Settings are no longer written to registry. They are now written to settings.ini in the data folder below the application folder.
- Temp files are now written to the temp folder below the application folder.
- CONFIG is no longer depending on the missing MFC71.DLL.
2005-12-03 (1.0.0.16)
- Support for the settings: AfterPrintProgram, GhostscriptFolder, Output, SettingsProgram, ShowPDF and WorkArea.
- CONFIG program to change settings.
2005-11-20 (1.0.0.10-2)
- Setup now also support Windows 2000 and 2003.
2005-11-17 (1.0.0.10)
Credits
Bullzip wants to send a special thanks to the people who help us make the products better.
 Afrikaans - Jacques Roux, Moolman Oliver, Raymond Botha
Afrikaans - Jacques Roux, Moolman Oliver, Raymond Botha Arabic (Saudi Arabia) - Salim Derguini, Ali Barrak
Arabic (Saudi Arabia) - Salim Derguini, Ali Barrak Bosnian translation - Adnan Miljkovic
Bosnian translation - Adnan Miljkovic Bulgarian translation - Martin Kostov, Alexander Dimitrov, Miro Igov
Bulgarian translation - Martin Kostov, Alexander Dimitrov, Miro Igov Catalan translation - Cesc Beltran, lluis Jaime López, Ignasi Lluch
Catalan translation - Cesc Beltran, lluis Jaime López, Ignasi Lluch Chinese (Simplified) translation - Adamson Huang, Stephen Chan, Hua Dong
Chinese (Simplified) translation - Adamson Huang, Stephen Chan, Hua Dong Chinese (Traditional) translation - Adamson Huang, James from Taiwan, Wolf Chou
Chinese (Traditional) translation - Adamson Huang, James from Taiwan, Wolf Chou Croatian translation - Ante Spajic
Croatian translation - Ante Spajic Czech translation - Janoušek Ivo, Petr Å koda, Pavel Poles
Czech translation - Janoušek Ivo, Petr Å koda, Pavel Poles Dutch translation - Peter Vleeshakker, Koen Van Hoeck, Michiel, Dries Deronde
Dutch translation - Peter Vleeshakker, Koen Van Hoeck, Michiel, Dries Deronde Galician translation - Ricardo Santiago Mozos
Galician translation - Ricardo Santiago Mozos Esperanto translation - Vitor Luiz Rigoti dos Anjos
Esperanto translation - Vitor Luiz Rigoti dos Anjos Estonian translation - Aigari Kammer
Estonian translation - Aigari Kammer French translation - David Albertini, Laurent Quenette, Sylvain Ménard, Pierre le Lidgeu
French translation - David Albertini, Laurent Quenette, Sylvain Ménard, Pierre le Lidgeu Finnish translation - Aleksi Heinonen, Juuso Takalainen
Finnish translation - Aleksi Heinonen, Juuso Takalainen German translation - Dominik Kleine, Andreas Brenner, Michael Hüthe, Alexander Strauß, Melanie Breuer
German translation - Dominik Kleine, Andreas Brenner, Michael Hüthe, Alexander Strauß, Melanie Breuer Greek translation - Costas Stefanatos
Greek translation - Costas Stefanatos Hebrew translation - Omri Raisman, Assaf Prussak, Shimmy Weitzhandler, Dan Maxim
Hebrew translation - Omri Raisman, Assaf Prussak, Shimmy Weitzhandler, Dan Maxim Hungarian translation - Krisztian Hegedus, Adam Vegh, Kladek András
Hungarian translation - Krisztian Hegedus, Adam Vegh, Kladek András Indonesian translation - Pandu E Poluan, Wempi Naviera
Indonesian translation - Pandu E Poluan, Wempi Naviera Italian translation - Giampaolo Frello, Marco Ardito, Alessio Bottazzi, Gino Zamprogna, Graziano Rossi, Davide Cremonesi, Enrico Galletti
Italian translation - Giampaolo Frello, Marco Ardito, Alessio Bottazzi, Gino Zamprogna, Graziano Rossi, Davide Cremonesi, Enrico Galletti Japanese translation - Nardog, Masayuki Nozawa, Koba Takeshi, T. Maeda
Japanese translation - Nardog, Masayuki Nozawa, Koba Takeshi, T. Maeda Korean translation - ekdrms211, Shostakovich
Korean translation - ekdrms211, Shostakovich Latvian translation - Zagorskis Edgars, Peter Brasla
Latvian translation - Zagorskis Edgars, Peter Brasla Norwegian translation - Øystein Toen, Espen Fosse, Haakon R. Lockert
Norwegian translation - Øystein Toen, Espen Fosse, Haakon R. Lockert Norwegian (nynorsk) translation - Espen Fosse
Norwegian (nynorsk) translation - Espen Fosse Polish translation - Tomasz Kossut, Damian, Rafal Siedlak, Michal Brozyna
Polish translation - Tomasz Kossut, Damian, Rafal Siedlak, Michal Brozyna Portuguese (Brazil) translation - Paulo Neto, Mauricio Almeida, Ivan Pereira, Alvaro Jose Abackerli, Daniel de Freitas Leite
Portuguese (Brazil) translation - Paulo Neto, Mauricio Almeida, Ivan Pereira, Alvaro Jose Abackerli, Daniel de Freitas Leite Portuguese (Portugal) translation - Luís Barreto, Rui Lima de Almeida
Portuguese (Portugal) translation - Luís Barreto, Rui Lima de Almeida Russian translation - Andrey Baranov, Jura Gura, Josef Viller, Alexander Khabarov, Kalashnikoff Evgeny
Russian translation - Andrey Baranov, Jura Gura, Josef Viller, Alexander Khabarov, Kalashnikoff Evgeny Romanian translation - Stefan Savu, Ciprian Junca
Romanian translation - Stefan Savu, Ciprian Junca Serbian translation - Sasa Stojanovic, Igor Stanisic
Serbian translation - Sasa Stojanovic, Igor Stanisic Slovak translation - Janoušek Ivo, Tomas Hasko, Stanislava Jurinova
Slovak translation - Janoušek Ivo, Tomas Hasko, Stanislava Jurinova Slovenian translation - Tic Tomaž Bric
Slovenian translation - Tic Tomaž Bric Spanish translation - Tito Berli, Jason Becker, Felipe Lugo, David Cantón, Ivan Vojvodic, Gustavo del Dago
Spanish translation - Tito Berli, Jason Becker, Felipe Lugo, David Cantón, Ivan Vojvodic, Gustavo del Dago Swedish translation - Fredrik Fagerlund, Björn Rydh, Karl-Johan Pantzar, Christian Andersson
Swedish translation - Fredrik Fagerlund, Björn Rydh, Karl-Johan Pantzar, Christian Andersson Thai translation - Manoch Somsax
Thai translation - Manoch Somsax Turkish translation - Can Guldogan, Can Sayin, Mustafa Çelebi, Ersan Alfan, Serkan Taş
Turkish translation - Can Guldogan, Can Sayin, Mustafa Çelebi, Ersan Alfan, Serkan Taş Ukrainian translation - Alexander Khabarov, Svyatoslav Potyeyenko
Ukrainian translation - Alexander Khabarov, Svyatoslav Potyeyenko Vietnamese translation - Nguyen Thi Huyen Trang, Long Nguyen Vinh
Vietnamese translation - Nguyen Thi Huyen Trang, Long Nguyen Vinh
Additional Resources
Examples
User Contributions
Sponsors
Visual Basic .NET
 | |
| Paradigm | Structured, imperative, object-oriented, declarative, generic, reflective and event-driven |
|---|---|
| Designed by | Microsoft |
| Developer | Microsoft |
| First appeared | 2001; 19 years ago (2001) |
| Stable release | 2019 (16.0) / July 24, 2019; 13 months ago (2019-07-24) |
| Typing discipline | Static, both strong and weak,[1]both safe and unsafe,[1]nominative |
| Platform | .NET Framework, Mono, .NET Core 3[2] |
| OS | Chiefly Windows Also on Android, BSD, iOS, Linux, macOS, Solaris and Unix |
| License | Roslyn compiler: Apache License 2.0[3] |
| Filename extensions | |
| Website | docs.microsoft.com/dotnet/visual-basic/ |
| Major implementations | |
| .NET Framework SDK, Roslyn Compiler and Mono | |
| Dialects | |
| Microsoft Visual Basic | |
| Influenced by | |
| Visual Basic | |
| Influenced | |
| Small Basic | |
Visual Basic .NET (VB.NET) is a multi-paradigm, object-orientedprogramming language, implemented on the .NET Framework. Microsoft launched VB.NET in 2002 as the successor to its original Visual Basic language. Although the ".NET" portion of the name was dropped in 2005, this article uses "Visual Basic [.NET]" to refer to all Visual Basic languages released since 2002, in order to distinguish between them and the classic Visual Basic. Along with Visual C#, it is one of the two main languages targeting the .NET framework.
Microsoft's integrated development environment (IDE) for developing in Visual Basic .NET language is Visual Studio. Most Visual Studio editions are commercial; the only exceptions are Visual Studio Express and Visual Studio Community, which are freeware. In addition, the .NET Framework SDK includes a freeware command-linecompiler called vbc.exe. Mono also includes a command-line VB.NET compiler.
Syntax[edit]
 | This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it.(April 2014) |
VB.NET uses statements to specify actions. The most common statement is an expression statement, consisting of an expression to be evaluated, on a single line. As part of that evaluation, functions or subroutines may be called and variables may be assigned new values. To modify the normal sequential execution of statements, VB.NET provides several control-flow statements identified by reserved keywords. Structured programming is supported by several constructs including two conditional execution constructs ( … … … and ... ... ) and three iterative execution (loop) constructs ( … , … , and ) . The … statement has separate initialisation and testing sections, both of which must be present. (See examples below.) The statement steps through each value in a list.
In addition, in Visual Basic .NET:
- There is no unified way of defining blocks of statements. Instead, certain keywords, such as "If … Then" or "Sub" are interpreted as starters of sub-blocks of code and have matching termination keywords such as "End If" or "End Sub".
- Statements are terminated either with a colon (":") or with the end of line. Multiple-line statements in Visual Basic .NET are enabled with " _" at the end of each such line. The need for the underscore continuation character was largely removed in version 10 and later versions.[4]
- The equals sign ("=") is used in both assigning values to variables and in comparison.
- Round brackets (parentheses) are used with arrays, both to declare them and to get a value at a given index in one of them. Visual Basic .NET uses round brackets to define the parameters of subroutines or functions.
- A single quotation mark (') or the keyword , placed at the beginning of a line or after any number of space or tab characters at the beginning of a line, or after other code on a line, indicates that the (remainder of the) line is a comment.
Simple example[edit]
The following is a very simple VB.NET program, a version of the classic "Hello, World!" example created as a console application:
It prints "Hello, World!" on a command-line window. Each line serves a specific purpose, as follows:
This is a module definition. Modules are a division of code, which can contain any kind of object, like constants or variables, functions or methods, or classes, but can't be instantiated as objects like classes and cannot inherit from other modules. Modules serve as containers of code that can be referenced from other parts of a program.[5]
It is common practice for a module and the code file which contains it to have the same name. However, this is not required, as a single code file may contain more than one module and/or class.
This line defines a subroutine called "Main". "Main" is the entry point, where the program begins execution.[6]
This line performs the actual task of writing the output. Console is a system object, representing a command-line interface (also known as a "console") and granting programmatic access to the operating system's standard streams. The program calls the Console method WriteLine, which causes the string passed to it to be displayed on the console.
Instead of Console.WriteLine, one could use MsgBox, which prints the message in a dialog box instead of a command-line window.[7]
Complex example[edit]
This piece of code outputs Floyd's Triangle to the console:
Comparison with the classic Visual Basic[edit]
Whether Visual Basic .NET should be considered as just another version of Visual Basic or a completely different language is a topic of debate. There are new additions to support new features, such as structured exception handling and short-circuited expressions. Also, two important data-type changes occurred with the move to VB.NET: compared to Visual Basic 6, the data type has been doubled in length from 16 bits to 32 bits, and the data type has been doubled in length from 32 bits to 64 bits. This is true for all versions of VB.NET. A 16-bit integer in all versions of VB.NET is now known as a . Similarly, the Windows Forms editor is very similar in style and function to the Visual Basic form editor.
The things that have changed significantly are the semantics—from those of an object-based programming language running on a deterministic, reference-counted engine based on COM to a fully object-oriented language backed by the .NET Framework, which consists of a combination of the Common Language Runtime (a virtual machine using generational garbage collection and a just-in-time compilation engine) and a far larger class library. The increased breadth of the latter is also a problem that VB developers have to deal with when coming to the language, although this is somewhat addressed by the My feature in Visual Studio 2005.
The changes have altered many underlying assumptions about the "right" thing to do with respect to performance and maintainability. Some functions and libraries no longer exist; others are available, but not as efficient as the "native" .NET alternatives. Even if they compile, most converted Visual Basic 6 applications will require some level of refactoring to take full advantage of the new language. Documentation is available to cover changes in the syntax, debugging applications, deployment and terminology.[8]
Comparative examples[edit]
The following simple examples compare VB and VB.NET syntax. They assume that the developer has created a form, placed a button on it and has associated the subroutines demonstrated in each example with the click event handler of the mentioned button. Each example creates a "Hello, World" message box after the button on the form is clicked.
Visual Basic 6:
VB.NET (MsgBox or MessageBox class can be used):
- Both Visual Basic 6 and Visual Basic .NET automatically generate the and statements when the corresponding button is double-clicked in design view. Visual Basic .NET will also generate the necessary and statements. The developer need only add the statement to display the "Hello, World" message box.
- All procedure calls must be made with parentheses in VB.NET, whereas in Visual Basic 6 there were different conventions for functions (parentheses required) and subs (no parentheses allowed, unless called using the keyword ).
- The names and are not obligatory. However, these are default names for a command button in Visual Basic 6 and VB.NET respectively.
- In VB.NET, the keyword is used to make the sub a handler for the event of the object . In Visual Basic 6, event handler subs must have a specific name consisting of the object's name ("Command1"), an underscore ("_"), and the event's name ("Click", hence "Command1_Click").
- There is a function called in the namespace which can be used (instead of ) similarly to the corresponding function in Visual Basic 6. There is a controversy[9] about which function to use as a best practice (not only restricted to showing message boxes but also regarding other features of the namespace). Some programmers prefer to do things "the .NET way", since the Framework classes have more features and are less language-specific. Others argue that using language-specific features makes code more readable (for example, using (C#) or (VB.NET) instead of ).
- In Visual Basic 2008, the inclusion of has become optional.
The following example demonstrates a difference between Visual Basic 6 and VB.NET. Both examples close the active window.
Visual Basic 6:
VB.NET:
The 'cmd' prefix is replaced by the 'btn' prefix, conforming to the new convention previously mentioned.[which?]
Visual Basic 6 did not provide common operator shortcuts. The following are equivalent:
Visual Basic 6:
VB.NET:
Comparison with C#[edit]
C# and Visual Basic .NET are Microsoft's first languages made to program on the .NET Framework (later adding F# and more; others have also added languages). Though C# and VB.NET are syntactically different, that is where the differences mostly end. Microsoft developed both of these languages to be part of the same .NET Framework development platform. They are both developed, managed, and supported by the same language development team at Microsoft.[10] They compile to the same intermediate language (IL), which runs against the same .NET Framework runtime libraries.[11] Although there are some differences in the programming constructs, their differences are primarily syntactic and, assuming one avoids the Visual Basic "Compatibility" libraries provided by Microsoft to aid conversion from Visual Basic 6, almost every feature in VB has an equivalent feature in C# and vice versa. Lastly, both languages reference the same Base Classes of the .NET Framework to extend their functionality. As a result, with few exceptions, a program written in either language can be run through a simple syntax converter to translate to the other. There are many open source and commercially available products for this task.
Examples[edit]
Hello World![edit]
Windows Form Application[edit]
Requires a button called Button1.

Console Application[edit]
Speaking[edit]
Windows Form Application[edit]
Requires a TextBox titled 'TextBox1' and a button called Button1.
Console Application[edit]
Version history[edit]
Succeeding the classic Visual Basic version 6.0, the first version of Visual Basic .NET debuted in 2002. As of 2020[update], ten versions of Visual Basic .NET are released.
2002 (VB 7.0)[edit]
The first version, Visual Basic .NET, relies on .NET Framework 1.0. The most important feature is managed code, which contrasts with the classic Visual Basic.
2003 (VB 7.1)[edit]
Visual Basic .NET 2003 was released with .NET Framework 1.1. New features included support for the .NET Compact Framework and a better VB upgrade wizard. Improvements were also made to the performance and reliability of .NET IDE (particularly the background compiler) and runtime. In addition, Visual Basic .NET 2003 was available in the Visual Studio.NET Academic Edition, distributed to a certain number of scholars[weasel words] from each country without cost.
2005 (VB 8.0)[edit]
After Visual Basic .NET 2003, Microsoft dropped ".NET" from the name of the product, calling the next version Visual Basic 2005.
For this release, Microsoft added many features intended to reinforce Visual Basic .NET's focus as a rapid application development platform and further differentiate it from C#., including:
- Edit and Continue feature[further explanation needed]
- Design-time expression evaluation[further explanation needed]
- A pseudo-namespace called "My", which provides:[12][13]
- Easy access to certain areas of the .NET Framework that otherwise require significant code to access like using rather than
- Dynamically generated classes (e.g. My.Forms)
- Improved VB-to-VB.NET converter[14]
- A "using" keyword, simplifying the use of objects that require the Dispose pattern to free resources
- Just My Code feature, which hides (steps over) boilerplate code written by the Visual Studio .NET IDE and system library code during debugging
- Data Source binding, easing database client/server development
To bridge the gaps between itself and other .NET languages, this version added:
Visual Basic 2005 introduced the operator that makes equivalent to . It gained notoriety[17] when it was found to be the subject of a Microsoft patent application.[18][19]
2008 (VB 9.0)[edit]
Visual Basic 9.0 was released along with .NET Framework 3.5 on November 19, 2007.
For this release, Microsoft added many features, including:
2010 (VB 10.0)[edit]
In April 2010, Microsoft released Visual Basic 2010. Microsoft had planned to use Dynamic Language Runtime (DLR) for that release[20] but shifted to a co-evolution strategy between Visual Basic and sister language C# to bring both languages into closer parity with one another. Visual Basic's innate ability to interact dynamically with CLR and COM objects has been enhanced to work with dynamic languages built on the DLR such as IronPython and IronRuby.[21] The Visual Basic compiler was improved to infer line continuation in a set of common contexts, in many cases removing the need for the " _" line continuation characters. Also, existing support of inline Functions was complemented with support for inline Subs as well as multi-line versions of both Sub and Function lambdas.[22]
2012 (VB 11.0)[edit]
Visual Basic 2012 was released alongside .NET Framework 4.5. Major features introduced in this version include:[further explanation needed]
- Asynchronous programming with "async" and "await" statements
- Iterators
- Call hierarchy
- Caller information
- "Global" keyword in "namespace" statements
2013 (VB 12.0)[edit]
Visual Basic 2013 was released alongside .NET Framework 4.5.1 with Visual Studio 2013. Can also build .NET Framework 4.5.2 applications by installing Developer Pack.[23]
2015 (VB 14.0)[edit]
Visual Basic 2015 (code named VB "14.0") was released with Visual Studio 2015. Language features include a new "?." operator to perform inline null checks, and a new string interpolation feature is included to format strings inline.[24]
2017 (VB 15.x)[edit]
Visual Basic 2017 (code named VB "15.0") was released with Visual Studio 2017. Extends support for new Visual Basic 15 language features with revision 2017, 15.3, 15.5, 15.8. Introduces new refactorings that allow organizing source code with one action.[25][26]
2019 (VB 16.0)[edit]
Visual Basic 2019 (code named VB "16.0") was released with Visual Studio 2019. [27] The first version of Visual Basic focused on .NET Core.[28]
Cross-platform and open-source development[edit]
The official VB.NET compiler is written in VB.NET and is available on GitHub as a part of the .NET Compiler platform.[29] The creation of open-source tools for VB.NET development has been slow compared to C#, although the Mono development platform provides an implementation of VB.NET-specific libraries and a VB.NET 8.0 compatible compiler written in VB.NET,[30] as well as standard framework libraries such as Windows Forms GUI library.
SharpDevelop and MonoDevelop are open-source alternative IDEs. The Gambas environment is also similar but distinct from Visual Basic.
See also[edit]
References[edit]
- ^ ab"Option Explicit and Option Strict in Visual Basic .NET and in Visual Basic". Support. Microsoft. March 19, 2008. Retrieved August 22, 2013.
- ^Dollard, Kathleen. "Visual Basic in .NET Core 3.0". blogs.msdn.microsoft.com.
- ^https://github.com/dotnet/roslyn/blob/1ff27b046b5c03abb38bfeda44eb82da0b8df9de/License.txt
- ^"New Features in Visual Basic 10".
- ^"Module Statement". MSDN – Developer Center. Retrieved January 20, 2010.
- ^"Main Procedure in Visual Basic". MSDN – Developer Center. Retrieved January 20, 2010.
- ^"Visual Basic Version of Hello, World". MSDN – Developer Center. Retrieved January 20, 2010.
- ^"Microsoft Visual Basic 6.0 Migration Resource Center". MSDN. Microsoft. Retrieved November 9, 2014.
- ^"Visual Studio 2003 Retired Technical documentation". Microsoft Download Center.
- ^Krill, Paul (February 27, 2009). "Microsoft converging programming languages | Developer World". InfoWorld. Archived from the original on January 26, 2013. Retrieved August 18, 2013.
- ^"Microsoft Intermediate Language". Dotnet-guide.com. Retrieved August 18, 2013.
- ^Mackenzie, Duncan (2006). "Navigate The .NET Framework And Your Projects With The My Namespace". MSDN Magazine Visual Studio 2005 Guided Tour 2006. Microsoft.
- ^Whitney, Tyler (November 2005). "My.Internals: Examining the Visual Basic My Feature". MSDN. Microsoft.
- ^"What's New with the Visual Basic Upgrade Wizard in Visual Basic 2005". msdn2.microsoft.com.
- ^"Defining and Using Generics in Visual Basic 2005". msdn2.microsoft.com.
- ^"Operator Overloading in Visual Basic 2005". msdn2.microsoft.com.
- ^Sherriff, Lucy (February 22, 2005). "Real Software slams MS IsNot patent application". The Register. Retrieved April 6, 2009.
- ^Taft, Darryl K. (February 21, 2005). "Real Software Slams Microsofts Patent Effort". eWeek. Retrieved April 6, 2009.
- ^Vick, Paul A. Jr.; Barsan, Costica Corneliu; Silver, Amanda K. (May 14, 2003). "United States Patent Application: 20040230959". Patent Application Full Text and Image Database. US Patent & Trademark Office. Retrieved April 6, 2009.
- ^"What the heck is "VBx"?". May 1, 2007. Retrieved August 12, 2009.
- ^"What is New in Visual Basic 2010". Microsoft. 2009. Retrieved August 12, 2009.
- ^"What's New in Visual Basic 2010". Microsoft. 2010. Retrieved August 1, 2010.
- ^Download Microsoft .NET Framework 4.5.2 Developer Pack for Windows Vista SP2, Windows 7 SP1, Windows 8, Windows 8.1, Windows Server 2008 SP2 Windows Server 2008 R2 SP1, Windows Server 2012 and Windows Server 2012 R2 from Official Microsoft Download Center
- ^"New Language Features in Visual Basic 14". msdn.com.
- ^reshmim. "Visual Studio 2017 Release Notes". www.visualstudio.com.
- ^reshmim. "What's new for Visual Basic 2017,15.3,15.5,15.8". www.visualstudio.com.
- ^reshmim. "Visual Studio 2019 Release Notes". www.visualstudio.com.
- ^reshmim. "What's new for Visual Basic 16.0". www.visualstudio.com.
- ^Roslyn, .NET Foundation, April 13, 2019, retrieved April 14, 2019
- ^"Redirecting…". www.mono-project.com.
Further reading[edit]
External links[edit]
 | Wikiversity has learning resources about VB.NET |
Dialects of the BASIC programming language (list) | |
|---|---|
| Classic | |
What’s New in the VB.Net to C Sharp Converter 1.3 serial key or number?
Screen Shot
System Requirements for VB.Net to C Sharp Converter 1.3 serial key or number
- First, download the VB.Net to C Sharp Converter 1.3 serial key or number
-
You can download its setup from given links:


